Calculating Interest Expense: A Step-by-Step Guide
In simple terms, interest expense is the cost you pay for borrowing money. It’s like renting a movie—only instead of paying for a night’s worth of entertainment, you’re paying for the use of someone else’s cash.
Now, let me tell you a little story. Back in the day, when I first dipped my toes into the world of finance, the term “interest expense” was like a foreign language to me. I’d stare at the numbers and formulas, feeling more lost than a tourist without a map. But, as I began to unravel its mysteries, I realized that understanding interest expense wasn’t just about crunching numbers—it was a key to unlocking better financial management skills.
By learning to calculate my own interest expenses, I could make smarter decisions about loans, investments, and business finances. It was like having a superpower! And guess what? By the end of this guide, you’ll have that superpower too.
Key Takeaways
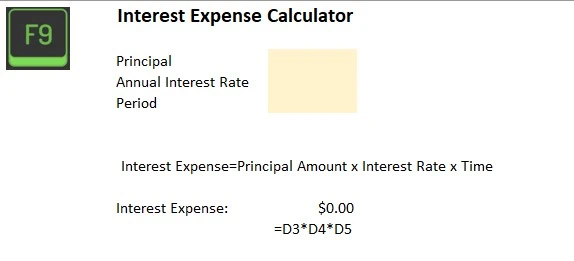
- Annual interest expense is calculated using the formula: Principal Amount x Annual Interest Rate x Time Period. Remember, the time period should be in years and the interest rate should be the annual rate.
- Interest expense impacts your income statement by reducing your net income. On the balance sheet, it indirectly affects your liabilities and equity section. And on the cash flow statement, it’s categorized under operating activities, affecting your overall cash flow.
The Basics of Interest Expense
Alright, let’s get down to the nitty-gritty: the basics of interest expense. In a business context, interest expense is the cost of borrowing money. It’s most commonly associated with loans, credit cards, or debt financing. Every time you take out a loan, or use credit to fund your business operations, you’re signing up to pay interest expense.
Now, let’s imagine you’re at a pizza party. Everyone’s having a good time, and there’s a delicious, cheesy pizza on the table. You didn’t bring this pizza, but you’re more than welcome to have a slice. However, for every slice you take, you owe the pizza owner a bite from your own sandwich in return. That returned bite? That’s like your interest expense. You’re enjoying something now (the borrowed money), but you’ll have to give something back later (the interest).
Why is understanding this pizza…err…interest expense so important? Well, it’s pretty simple. Interest expense can significantly impact your bottom line. The more you borrow, the more interest expense you’ll accrue, which can eat into your profits just like those pizza slices at the party. If you don’t keep an eye on it, you might find that you’ve promised away all your sandwich bites without realizing it!
Step-by-Step Guide to Calculating Interest Expense
Make sure to download our free excel calculator for interest expense to follow along:
Step 1: Identifying Your Loan Details
First things first, we need to gather some details about your loan. You’ll need to know the outstanding principal amount (that’s the original amount you borrowed minus any payments), the annualized interest rate, and the period for which the money is borrowed. You can usually find these details in your loan agreement or on your bank’s website.

Step 2: Understanding the Formula
Next, we have to get familiar with the interest expense formula. It’s actually pretty simple: Interest Expense = Principal Amount x Interest Rate x Time.
Step 3: Applying the Formula
Now, it’s time to put our aprons on and start baking…err…calculating. Let’s say we have an average debt balance of $10,000 with an annual interest rate of 5%, borrowed for 2 year2. Plugging these numbers into our formula, we get: Interest Expense = $10,000 x 0.05 x 2, which equals $1,000.

Accounting for Interest Expense
Now that we understand what interest expense represents and how to calculate it, let’s uncover how it impacts your financial statements and how to record it in your books.
How Interest Expense Appears On Each of the Financial Statements
Think of your financial statements as a snapshot of your business’s financial health. It’s like taking a selfie—only instead of capturing your best angle, it captures your business’s financial status.
First up, we have the income statement. Here, interest expense is like that pesky pimple that shows up right before picture day—it reduces your net income. The more interest you pay, the smaller your profits look in the snapshot.
Next, we have the balance sheet. Your interest expense doesn’t directly affect this statement, but it does indirectly influence your liabilities and equity section. Rather, your borrowed funds sit in a line item on a liability account.
Lastly, we have the cash flow statement. Here, interest expense is categorized under operating activities, just like how your breathing rate would be categorized under ‘vital signs’ in a medical report. It’s a necessary expense that affects your overall cash flow.
Journaling Interest Expense

Now, onto the exciting world of journal entries! Journaling interest expense is like keeping a diary of all the slices of pizza (remember our pizza analogy?) you owe.
When you incur interest payments, your journal entry should debit (increase) your company’s interest expense account and credit (increase) your interest payable account. It’s like writing in your diary, “Owe Tom one pizza slice.”
Later, when you pay off the interest incurred, you flip the script. You debit (decrease) your interest payable account and credit (decrease) your cash account. Essentially, you’re saying, “Paid Tom his pizza slice.”
Common Mistakes & How to Avoid Them
1. Mixing up the Interest Rate:
Sometimes, people confuse the annual interest rate with the monthly or quarterly rate. Remember, our formula needs the annual rate. It’s like confusing tablespoons with teaspoons when you’re baking – it can make a HUGE difference to the final outcome!
How to Avoid: Always double-check your interest rate and ensure it’s the annual one. If it’s not, convert it by multiplying the monthly rate by 12, or the quarterly rate by 4. You’ve got this!
2. Ignoring the Time Period:
Another common blunder is neglecting the time factor in the formula. If you borrow money for less than a year, you need to adjust the time accordingly. It’s like thinking your pizza will be ready in 15 minutes when it actually needs an hour in the oven.
How to Avoid: Make sure you correctly account for the time period in your calculations. If it’s less than a year, use a fraction (e.g., half a year is 0.5). Keep your eye on the clock – or in this case, the calendar!
3. Overborrowing:
Interest rates may seem insignificant, but they can add up quickly if you’re not careful. Overborrowing means taking on more debt than you can afford to pay back comfortably, resulting in higher interest payments and potential financial strain.
How to Avoid: Track interest using the interest coverage ratio. The interest coverage ratio is calculated by taking a company’s operating income and dividing it by the total interest payments due. This will give you an idea of how well the company can handle its debt obligations.

Quick Recap
We’ve rummaged through loan agreements, whipped up some interest expense ‘cakes’, and even kept a pizza diary! Together, we’ve explored how to calculate interest expense, how it impacts your financial statements, how to record it, and learned how to avoid common mistakes.
But the real fun starts now! Think of what you’ve learned today as a new recipe. It’s time to get into your own finance kitchen and put it to the test. Try calculating your own interest expense, play around with different numbers, and see what happens. Remember, practice makes perfect – or in our case, perfect interest expense calculations!
Frequently Asked Questions
What is interest income and expense?
Interest income refers to the earnings you receive from lending money, such as interest received on a savings account or bonds. Interest expense, on the other hand, is the cost incurred for borrowing money. It’s like the fee you pay for using someone else’s money.
Does interest count as an expense?
Yes, interest does count as an expense. Just like paying rent for using someone’s property, you pay interest for using someone’s money. It’s considered an operating expense and is tax-deductible.
What is the formula for accrued interest expense?
The formula for accrued interest expense is similar to the regular interest expense formula: Principal Amount x Annual Interest Rate x Time Period. The difference is that the time period only includes the amount of time that has passed since the last payment.
How do you calculate monthly interest expense?
To calculate monthly interest expense, use the same formula but adjust the time period to reflect the number of months instead of years. So, it would be: Principal Amount x Annual Interest Rate x (Number of Months/12).
Have any questions? Are there other topics you would like us to cover? Leave a comment below and let us know! And make sure to subscribe to our Newsletter to receive exclusive financial news right to your inbox.

