Cracking the Code: An Easy Guide to the Acid Test Ratio
Hi there, fellow finance enthusiasts! I’m thrilled you’re joining me on this journey today. I’m just like you, a curious mind eager to decode the mysteries of financial ratios. I remember the first time I encountered the term ‘Acid Test Ratio’. It sounded like something out of a chemistry lab, not a financial statement!
But don’t worry, we’re not about to dive into a science experiment. The Acid Test Ratio (also known as the quick ratio) is, in fact, a crucial tool in the world of finance. It’s a bit like a financial litmus test, revealing a company’s ability to cover current liabilities. In other words, it helps us figure out how well a company can meet its short-term obligations using its most liquid assets—those that can be quickly converted into cash or cash equivalents.
Why is this important, you ask? Well, imagine being on a road trip with the fuel gauge broken. You wouldn’t know when you might run out of gas and end up stranded, right? The Quick Ratio is like that fuel gauge for a business. It tells you if the company has enough financial ‘fuel’ to keep running smoothly in the short term.
Over the years, I’ve come to appreciate the power of understanding financial ratios like the Acid Test Ratio. They’ve helped me make informed decisions, whether I’m investing in a new venture or advising a client on their business strategy. And now, I’m excited to share these insights with you.
Key Takeaways
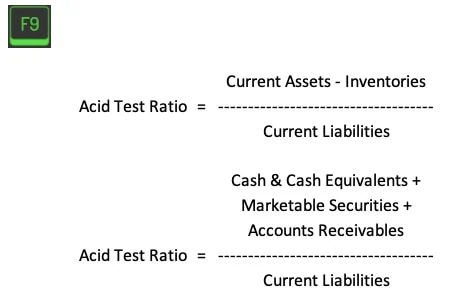
The Acid Test Ratio calculation is (Current Assets – Inventories) / Current Liabilities. Think of it as a recipe where you subtract the inventory (the flour you haven’t used yet) from the current assets (all your baking ingredients) and divide by the current liabilities (the cakes you’ve promised to bake).
Like Goldilocks and her porridge, you want the Acid Test / Quick Ratio to be just right—not too high, not too low, but around 1. A ratio less than 1 could signal potential liquidity problems, while a significantly higher ratio might imply underutilization of assets.
The Basics of Acid Test Ratio
Alright, friends, let’s dive into the nitty-gritty of the Acid Test Ratio. Picture this: you’re baking a cake (bear with me here, I promise this analogy will make sense!). To make the perfect cake, you need the right ingredients in the right proportions. Too much sugar or too little flour, and your cake might not come out as you’d hoped.
Similarly, the Acid Test Ratio is a financial ‘recipe’—it’s calculated by taking the most liquid current assets (cash, marketable securities, and accounts receivable) and dividing them by the current liabilities.
Acid Test Ratio Formula = (Cash + Marketable Securities + Accounts Receivable) / Current Liabilities
This ratio gives us an idea of how well a company can pay off its short-term debts using its quickest convertible-to-cash assets.
Now, you may be wondering, “Isn’t that similar to the current ratio?” Well spotted! But while they are both liquidity ratios (working capital ratio), here’s where our cake analogy comes in handy again. You see, the current ratio is like making a cake with all the ingredients you have at hand. On the other hand, the acid test ratio is like making a cake but without using eggs. It excludes inventory from the current assets because inventory isn’t as easily converted into cash. So, it’s a stricter measure of a company’s liquidity.
I remember when I first started exploring financial ratios, I used to mix up these two all the time. Once, during a meeting with a potential investor, I confidently explained the current ratio while referring to it as the acid test ratio. Imagine my embarrassment when he gently corrected me! We had a good laugh about it, and it taught me a valuable lesson: always double-check your financial ‘recipes’ before serving them up!
Step-by-Step Guide to Calculating the Acid Test Ratio
Hello again, my finance aficionados! Now that we’ve got our heads around what the Acid Test Ratio is, let’s roll up our sleeves and get our hands dirty with some financial ‘baking’.
Remember our recipe? The Acid Test Ratio = (Current Assets – Inventories) / Current Liabilities. It’s a simple formula, but like any recipe, it’s all about using the right ingredients in the right proportions.
The following items can all be found on a company’s balance sheet:
- Cash and cash equivalents are the most liquid current assets on a company’s balance sheet and include checking accounts, saving accounts, or term deposits/bonds with less than a 3-month maturity
- Marketable securities are financial instruments that can be readily converted into cash
- Accounts receivables are the amounts owed to a company for providing customers with goods or services.
- Current liabilities are accounts payable, short term debt, and other obligations due within one year.
Let’s walk through this together with a real-life example. Say hello to our imaginary company, ‘Bake & Shake Ltd.’ Here are some numbers from their balance sheet:
- Current Assets: $500,000
- Inventories: $200,000
- Current Liabilities: $300,000
To calculate the Acid Test Ratio, we first subtract the inventories from the current assets. That gives us $500,000 – $200,000 = $300,000. Next, we divide this by the current liabilities, which are $300,000. So, $300,000 / $300,000 = 1.
Voila! This company’s acid test ratio is 1. This means they have exactly enough liquid assets to cover their short-term liabilities.
Now, it’s your turn to play financial chef! Take a look at General Motors‘ balance sheet below and try calculating their acid ratio. Don’t worry, I’ll still be here when you get back.

(Don’t peek below until you’ve tried!)
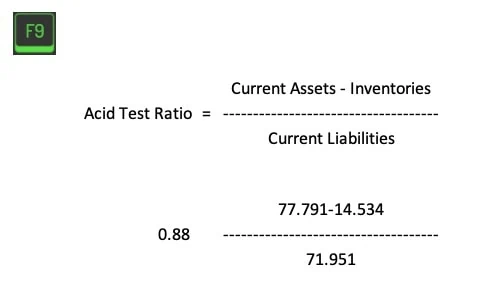
Done? Fantastic! How did that feel? Remember, it’s okay if you stumbled a bit. Like learning to flip pancakes, it might take a few tries to get this right. But don’t worry, with each attempt, you’re becoming more adept at understanding and managing business finances. Keep going, my friend, you’re doing great!
Interpreting Acid Test Ratios
Now that we’ve mastered the art of calculating the Acid Test Ratio, it’s time to understand what those numbers actually tell us. It’s like baking the perfect cake and then figuring out what the taste tells you about the ingredients used.
Firstly, an Acid Test Ratio of 1, like our friends at ‘Bake & Shake Ltd.’, means a company can meet its short-term obligations with its most liquid assets. It’s a comfortable spot to be in, like having just the right amount of flour for your cake.
The acid test ratio calculated a value greater than 1? Even better! This means the company has more than enough liquid assets to cover its short-term liabilities. It’s like having extra flour—you can bake another cake if you want to!
But what if the ratio is less than 1? Well, that’s a red flag. It indicates that the company might struggle to pay off its short-term debts—like trying to bake a cake without enough flour. Not ideal, right?
Now, here’s a practical tip: use the Acid Test Ratio as a tool to compare different companies within the same industry. It’s a great way to see who’s managing their finances better and could influence your investment decisions.
Let’s consider a real-life case study: During the 2008 financial crisis, many companies saw their Acid Test Ratios drop below 1 due to heavy debts and slow sales. But Amazon, with its diverse product range and robust online presence, maintained an Acid Test Ratio above 1 throughout the crisis. This was a clear indicator of Amazon’s strong liquidity position, even in tough times, making it an attractive option for investors.
Common Mistakes and Misconceptions
We’ve baked our financial cake, tasted it, and understood what it’s trying to tell us. But, like any baking journey, there are some common blunders we can make along the way. Let’s take a light-hearted look at these and learn how to sidestep them.
Firstly, the Acid Test Ratio is not a popularity contest. A higher ratio isn’t always better. Imagine adding too much sugar to your cake – sure it’s sweet, but you might also end up with a toothache! Similarly, an excessively high ratio might indicate that the company isn’t investing its excess cash efficiently.
Secondly, the Acid Test Ratio isn’t a crystal ball. It gives us insight into a company’s short-term liquidity, but it doesn’t predict the future. It’s like knowing how many eggs you have in your fridge right now—it tells you nothing about whether you’ll have any eggs next week.
Finally, remember that it’s not all about the Acid Test Ratio. Don’t fall into the trap of using it as your only measure of a company’s health. That would be like judging a cake based solely on its frosting—sure, it’s important, but there’s so much more to consider!
So, how do we avoid these pitfalls? Well, here are a few tips:
- Context is key: Always interpret the Acid Test Ratio in the context of the industry norms and the company’s historical performance.
- Use it as part of a balanced diet: The ratio is just one ingredient in your financial analysis recipe. Use it alongside other ratios for a well-rounded view.
- Don’t forget the long term: While the Acid Test Ratio is great for understanding short-term liquidity, don’t forget to consider long-term factors like growth potential and market trends.
Quick Recap
Well, my finance aficionados, we’ve done some serious financial baking together today! We’ve mixed, measured, and kneaded our way through the world of the Acid Test Ratio.
We started with a simple recipe: Acid Test Ratio = (Current Assets – Inventories) / Current Liabilities. We then put on our chef hats and calculated this ratio for our imaginary company, ‘Bake & Shake Ltd.’ Next, we tasted and interpreted our results, learning what different Acid Test Ratio values tell us about a company’s financial health.
Along the way, we also stumbled upon some common mistakes and misconceptions. But hey, who doesn’t love a good kitchen mishap story? More importantly, we learned how to avoid these blunders and make the most of our Acid Test Ratio knowledge.
Now, it’s your turn to step into the kitchen. Use this newfound knowledge to whip up some financial insight for your own business or investments. Remember, the Acid Test Ratio is just one dish in your financial cuisine—make sure to explore other dishes as well.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is an acid test ratio of 1.5 good?
Yes, a company’s Acid Test Ratio of 1.5 is considered good. It means the company has 1.5 times the amount of quick assets as its current liabilities, indicating it can comfortably meet its short-term obligations using its most liquid assets.
What does acid test ratio indicate?
The Acid Test Ratio indicates a company’s ability to pay off its immediate liabilities without needing to sell its inventory. It’s like having enough money in your wallet to buy your morning coffee without having to sell your favorite mug.
What Is The Difference Between The Quick Ratio And The Acid Test Ratio?
There isn’t a difference! They are two names for the same ratio.
What if acid test ratio is more than 2?
An very high ratio more than 2 signifies the company has twice the amount of its most liquid assets compared to its current liabilities. While it’s generally a good sign, it might also suggest that the company isn’t utilizing its assets efficiently, much like having a lot of extra flour but not baking enough cakes.
What is the formula for the acid test ratio in Excel?
In Excel the acid test ratio formula would be =(Cell with company’s Current Assets – Cell with Inventories) / Cell with Current Liabilities. Just replace the placeholders with the actual cell numbers, and voila—you’ve got your ratio!
Have any questions? Are there other topics you would like us to cover? Leave a comment below and let us know! Make sure to subscribe to our Newsletter to receive exclusive financial news right to your inbox.

